22.02.06 NMS(Non Maximum Suppression) 추가, 내용 추가
Opencv3.3.1부터 추가된 readNetFromDarknet() 함수를 사용하여
Yolo 네트워크 정보(cfg파일)와 학습된 가중치 정보(weights)를 불러올 수 있습니다.
OpenCV로 영상과 Yolo 모델을 읽어와서
읽은 영상 내의 물체를 검출합니다.
cfg와 weights파일은 아래 사이트에서 다운받으실 수 있습니다.
GitHub - AlexeyAB/darknet: YOLOv4 / Scaled-YOLOv4 / YOLO - Neural Networks for Object Detection (Windows and Linux version of Da
YOLOv4 / Scaled-YOLOv4 / YOLO - Neural Networks for Object Detection (Windows and Linux version of Darknet ) - GitHub - AlexeyAB/darknet: YOLOv4 / Scaled-YOLOv4 / YOLO - Neural Networks for Object ...
github.com
코드 설명
using namespace cv::dnn;
const float confidenceThreshold = 0.24f;
Net m_net;
std::string yolo_cfg = "./yolo/yolov4.cfg";
std::string yolo_weights = "./yolo/yolov4.weights";
m_net = readNetFromDarknet(yolo_cfg, yolo_weights);
m_net.setPreferableBackend(DNN_BACKEND_OPENCV);
m_net.setPreferableTarget(DNN_TARGET_CPU);
cv::Mat inputBlob = blobFromImage(img, 1 / 255.F, cv::Size(416, 416), cv::Scalar(), true, false); //Convert Mat to batch of images
m_net.setInput(inputBlob);
std::vector<cv::Mat> outs;
cv::Mat detectionMat = m_net.forward();OpenCV dnn 모듈을 활용하여 darknet cfg파일과 weights파일을 읽을 수 있습니다.
imread로 읽은 이미지는 blobFromImage 함수로 darknet에 입력되는 형태로 변경하여 setInput함수에 넣습니다.
그 다음 forward() 함수가 호출되면 추론 결과가 Mat 형태로 반환됩니다.
struct detectionResult
{
cv::Rect plateRect;
double confidence;
int type;
};
...
std::vector<detectionResult> vResultRect;
for (int i = 0; i < detectionMat.rows; i++)
{
const int probability_index = 5;
const int probability_size = detectionMat.cols - probability_index;
float* prob_array_ptr = &detectionMat.at<float>(i, probability_index);
size_t objectClass = std::max_element(prob_array_ptr, prob_array_ptr + probability_size) - prob_array_ptr;
float confidence = detectionMat.at<float>(i, (int)objectClass + probability_index);
if (confidence > confidenceThreshold)
{
float x_center = detectionMat.at<float>(i, 0) * (float)img.cols;
float y_center = detectionMat.at<float>(i, 1) * (float)img.rows;
float width = detectionMat.at<float>(i, 2) * (float)img.cols;
float height = detectionMat.at<float>(i, 3) * (float)img.rows;
cv::Point2i p1(round(x_center - width / 2.f), round(y_center - height / 2.f));
cv::Point2i p2(round(x_center + width / 2.f), round(y_center + height / 2.f));
cv::Rect2i object(p1, p2);
detectionResult tmp;
tmp.plateRect = object;
tmp.confidence = confidence;
tmp.type = objectClass;
vResultRect.push_back(tmp);
}
}
위의 최종 결과 행의 개수를 보면 당연히 많이 겹치는 바운딩 박스들이 검출됩니다.
겹치는 바운딩 박스 중복을 제거하기 위해(NMS) 구조체를 선언하고
구조체를 포함한 벡터에 바운딩 박스 위치, confidence, 클래스 분류 번호를 넣었습니다.
dokpin/yolov4_inference (github.com)
GitHub - dokpin/yolov4_inference
Contribute to dokpin/yolov4_inference development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
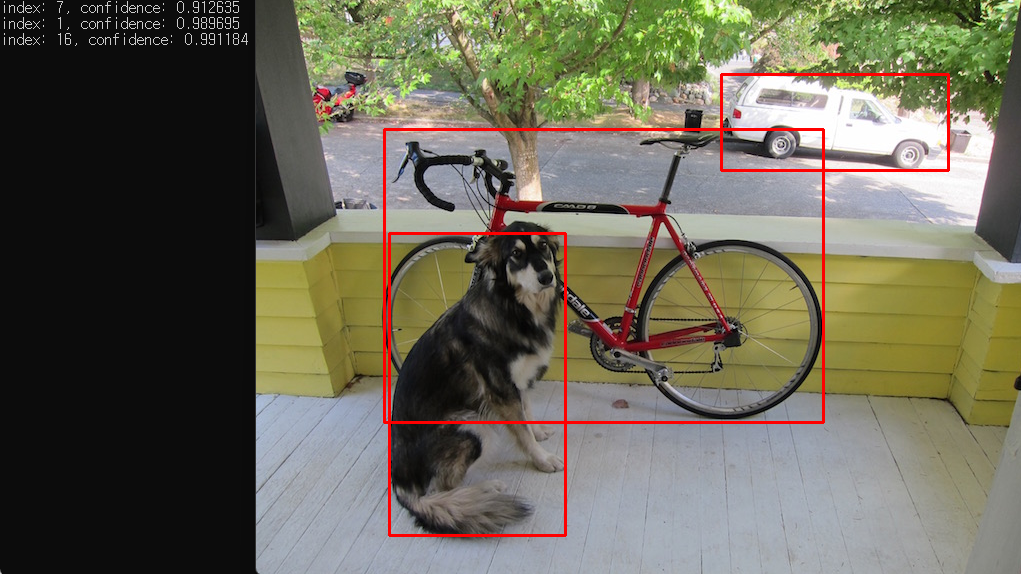
결과
'컴퓨터비전' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Yolo inference C++ example(VS2022+Darknet DLL) (1) | 2022.02.27 |
|---|---|
| Darknet + Visual Studio 2019,2022(C++ build) (0) | 2022.02.21 |
| NMS(Non Maximum Suppression) (0) | 2022.02.14 |
| 핀홀 카메라 모델(pinhole camera model) (0) | 2022.01.15 |
| Shortcut Layer (0) | 2021.11.28 |



